Encryption – Data encryption is the process of converting plain text data into an unreadable, encoded representation. After encrypted data has been decrypted, users and processes can read and process it.
- Encryption converts the data into an unusable form due to this there’s less chance of hacking and data theft.
- Plain text is scrambled by data encryption techniques so that only the person with the decryption key can read it.
- Personal Data or information that users receive, send, and save on mobile devices, is protected using the Data Encryption technique.
Types of Data Encryption
- There are 2 types of data encryption: Symmetric and Asymmetric encryption.
Symmetric Encryption- in this encryption a single, private password encrypts and decrypts data.
Asymmetric Encryption- also known as public-key encryption or public-key cryptography. In this encryption data is encrypted using a shared Public Key and data is decrypted using a private (non shared) key and that must be kept secret.
- Encryption and safe data handling can be done in a variety of ways. AES256 encryption is one of the most prevalent data security encryption algorithms.
How to Work with AES256
Encrypt Mechanism
- To encrypt and decode data on iOS, we can utilize the CommonCrypto library.
Step 1 – Add framework into the project.
Step 2 – Add Objective-C bridging header file.
![]()
Step 3 – Under the hood, this is a simple Crypter Struct that works with CommonCrypto.
protocol Randomizer {
static func randomIv() -> Data
static func randomSalt() -> Data
static func randomData(length: Int) -> Data
}
protocol Crypter {
func encrypt(_ digest: Data) throws -> Data
func decrypt(_ encrypted: Data) throws -> Data
}
struct AES256Crypter {
private var key: Data
private var iv: Data
public init(key: Data, iv: Data) throws {
guard key.count == kCCKeySizeAES256 else {
throw Error.badKeyLength
}
guard iv.count == kCCBlockSizeAES128 else {
throw Error.badInputVectorLength
}
self.key = key
self.iv = iv
}
enum Error: Swift.Error {
case keyGeneration(status: Int)
case cryptoFailed(status: CCCryptorStatus)
case badKeyLength
case badInputVectorLength
}
private func crypt(input: Data, operation: CCOperation) throws -> Data { var outLength = Int(0)
var outBytes = [UInt8](repeating: 0, count: input.count + kCCBlockSizeAES128) var status: CCCryptorStatus = CCCryptorStatus(kCCSuccess)
input.withUnsafeBytes { (encryptedBytes: UnsafePointer<UInt8>!) -> () in iv.withUnsafeBytes { (ivBytes: UnsafePointer<UInt8>!) in
key.withUnsafeBytes { (keyBytes: UnsafePointer<UInt8>!) -> () in status = CCCrypt(operation,
CCAlgorithm(kCCAlgorithmAES128), // algorithm
CCOptions(kCCOptionPKCS7Padding), // options
keyBytes, // key
key.count, // keylength
ivBytes, // iv
encryptedBytes, // dataIn
input.count, // dataInLength
&outBytes, // dataOut
outBytes.count, // dataOutAvailable
&outLength) // dataOutMoved
}
}
}
guard status == kCCSuccess else {
throw Error.cryptoFailed(status: status)
}
return Data(bytes: UnsafePointer<UInt8>(outBytes), count: outLength) }
static func createKey(password: Data, salt: Data) throws -> Data { let length = kCCKeySizeAES256
var status = Int32(0)
var derivedBytes = [UInt8](repeating: 0, count: length)
password.withUnsafeBytes { (passwordBytes: UnsafePointer<Int8>!) in salt.withUnsafeBytes { (saltBytes: UnsafePointer<UInt8>!) in
status = CCKeyDerivationPBKDF(CCPBKDFAlgorithm(kCCPBKDF2), // algorithm
passwordBytes, // password
password.count, // passwordLen
saltBytes, // salt
salt.count, // saltLen
CCPseudoRandomAlgorithm(kCCPRFHmacAlgSHA1), // prf 10000, // rounds
&derivedBytes, // derivedKey
length) // derivedKeyLen
}
}
guard status == 0 else {
throw Error.keyGeneration(status: Int(status))
}
return Data(bytes: UnsafePointer<UInt8>(derivedBytes), count: length) }
}
extension AES256Crypter: Crypter {
func encrypt(_ digest: Data) throws -> Data {
return try crypt(input: digest, operation: CCOperation(kCCEncrypt)) }
func decrypt(_ encrypted: Data) throws -> Data {
return try crypt(input: encrypted, operation: CCOperation(kCCDecrypt)) }
}
extension AES256Crypter: Randomizer {
static func randomIv() -> Data {
return randomData(length: kCCBlockSizeAES128)
}
static func randomSalt() -> Data {
return randomData(length: 8)
}
static func randomData(length: Int) -> Data {
var data = Data(count: length)
let status = data.withUnsafeMutableBytes { mutableBytes in
SecRandomCopyBytes(kSecRandomDefault, length, mutableBytes) }
assert(status == Int32(0))
return data
}
}
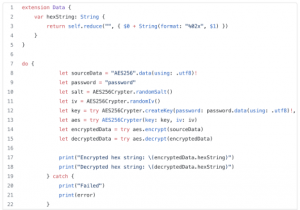
Step 4 – Use crypter where it’s needed.
 End to End Technology Solutions
End to End Technology Solutions
